Guided Wavelength Calculator
In the world of radio frequency (RF) and microwave engineering, understanding the concept of guided wavelength is crucial for designing efficient transmission lines, antennas, and waveguides. A Guided Wavelength Calculator is an essential tool that simplifies complex calculations, enabling engineers and students to determine the wavelength of signals propagating through a medium with a specific dielectric constant. In this article, we’ll explore what guided wavelength is, its importance, and how to use a guided wavelength calculator effectively.
What is Guided Wavelength Calculator?
Guided wavelength (λ<sub>g</sub>) refers to the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave as it propagates through a transmission line or waveguide, which is filled with a dielectric material. Unlike free-space wavelength, which is calculated in a vacuum, guided wavelength depends on the dielectric constant (ε<sub>r</sub>) of the medium. The formula to calculate guided wavelength is:

By combining these formulas, the guided wavelength can be determined for any frequency and dielectric constant.
Why is Guided Wavelength Important?
- Transmission Line Design: Guided wavelength is critical for designing transmission lines, such as microstrips and coaxial cables, to ensure impedance matching and minimize signal loss.
- Antenna Design: Antennas are often designed based on the wavelength of the signal they transmit or receive. Guided wavelength helps in optimizing antenna dimensions for specific frequencies.
- Waveguide Applications: In waveguides, the guided wavelength determines the cutoff frequency and the mode of propagation, which are essential for efficient signal transmission.
- RF and Microwave Circuits: Accurate calculation of guided wavelength is necessary for designing filters, resonators, and other RF components.
How to Use a Guided Wavelength Calculator?
A Guided Wavelength Calculator simplifies the process of calculating guided wavelength by automating the mathematical steps. Here’s how you can use it:
- Input Frequency: Enter the frequency of the signal. The calculator supports both GHz (gigahertz) and MHz (megahertz) units.
- Input Dielectric Constant: Provide the dielectric constant (ε<sub>r</sub>) of the medium. This value depends on the material used in the transmission line or waveguide.
- Calculate: Click the “Calculate” button to determine the guided wavelength.
- View Results: The calculator displays the guided wavelength in meters, centimeters, and millimeters for convenience.
Example Calculation
Let’s say you’re working with a signal frequency of 2.4 GHz and a dielectric constant of 4.6 (common for FR-4 PCB material). Using the guided wavelength formula:
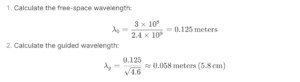
A guided wavelength calculator performs these steps instantly, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
Benefits of Using a Guided Wavelength Calculator
- Accuracy: Eliminates manual calculation errors, ensuring precise results.
- Efficiency: Saves time by automating complex calculations.
- Versatility: Supports multiple frequency units (GHz and MHz) and displays results in various units (meters, centimeters, millimeters).
- User-Friendly: Designed with a simple interface, making it accessible for both professionals and students.
Conclusion
A Guided Wavelength Calculator is an indispensable tool for anyone working with RF and microwave systems. By simplifying the calculation of guided wavelength, it enables engineers and students to focus on designing and optimizing their projects. Whether you’re working on transmission lines, antennas, or waveguides, understanding and using this tool can significantly enhance your efficiency and accuracy.
Also try: Horsepower to Weight Ratio Calculator
